- 📖 Geeky Medics OSCE Book
- ⚡ Geeky Medics Bundles
- ✨ 1300+ OSCE Stations
- ✅ OSCE Checklist PDF Booklet
- 🧠 UKMLA AKT Question Bank
- 💊 PSA Question Bank
- 💉 Clinical Skills App
- 🗂️ Flashcard Collections | OSCE, Medicine, Surgery, Anatomy
- 💬 SCA Cases for MRCGP
To be the first to know about our latest videos subscribe to our YouTube channel 🙌
In addition to knowing how to perform and interpret an arterial blood gas (ABG), it’s also important to understand how to appropriately document the results of an ABG in a patient’s notes. This guide provides a structured approach to documenting the findings of an ABG in a patient’s notes.
Documentation basics
Before we discuss how to document the findings of an ABG, we need to cover the basics that apply to all documentation in a patient’s notes. You can check out our detailed guide to writing in the notes for more information.
What should I use to write with?
You need to use a pen with black ink, as this is the most legible if notes are photocopied.
Patient details
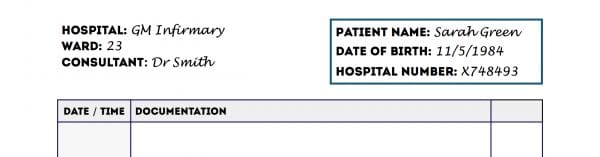
For every new sheet of paper, your first task should be to document at least three key identifiers for the relevant patient:
- Full name
- Date of birth
- Unique patient identifier
- Home address
If a patient label containing at least three identifiers is available, then this can be used instead of writing out the information manually.
Location details
You should indicate the patient’s current location on the continuation sheet:
- Hospital
- Ward
Beginning your entry in the notes
At this point, you should already be holding a pen with black ink and you should have ensured the continuation sheet has at least three key patient identifiers at the top.
The next documentation steps include:
1. Adding the date and time (in 24-hour format) of your entry.
2. Writing your name and role as an underlined heading.

Documenting the ABG results in the notes
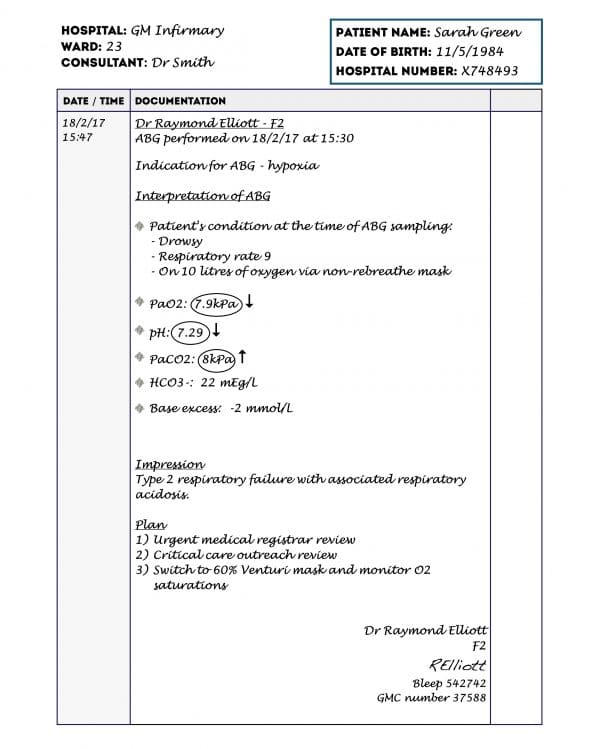
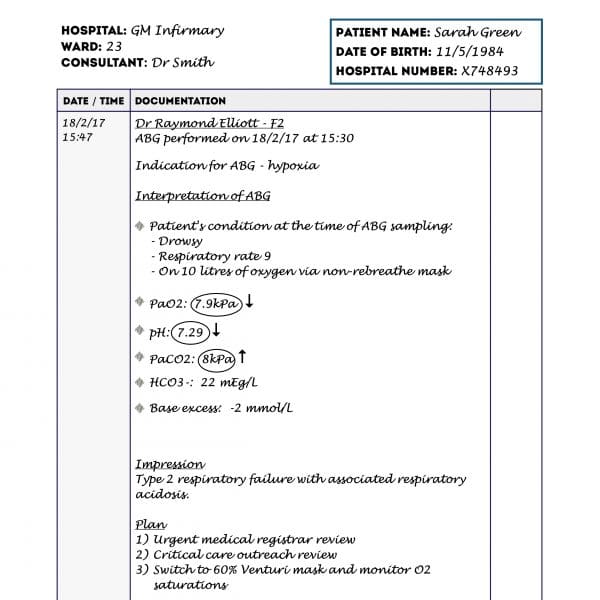
1. Document the time and date that the ABG was performed as this may be significantly different from the time you are documenting.
2. Write the indication for the ABG (e.g. hypoxia).
3. Document the ABG results and your interpretation of them (see our guide to ABG interpretation):
- A summary of the patient’s clinical condition when the ABG was performed (to provide some context for the results).
- PaO2: make sure to also document if the patient was on oxygen at the time the ABG was performed (including the flow rate and the oxygen delivery device).
- pH
- PaCO2
- HCO3–
- Base excess
If any of the results are abnormal you should highlight them, either by underlining or circling them. You can also indicate with an arrow whether the result is abnormally high or low.
4. Document your overall impression of the ABG (e.g. “metabolic acidosis with respiratory compensation”).
5. Document your plan based on the ABG findings.
Completing the entry in the notes
At the end of your entry to need to include the following:
- Your full name
- Your grade/role (e.g. F2/Medical Registrar)
- Your signature
- Your professional registration number (e.g. GMC number)
- Your contact number (e.g. phone/bleep)