- 📖 Geeky Medics OSCE Book
- ⚡ Geeky Medics Bundles
- ✨ 1300+ OSCE Stations
- ✅ OSCE Checklist PDF Booklet
- 🧠 UKMLA AKT Question Bank
- 💊 PSA Question Bank
- 💉 Clinical Skills App
- 🗂️ Flashcard Collections | OSCE, Medicine, Surgery, Anatomy
- 💬 SCA Cases for MRCGP
To be the first to know about our latest videos subscribe to our YouTube channel 🙌
Introduction
Anatomical planes are imaginary planes/2D surfaces used to divide the body to facilitate descriptions of location and movement.
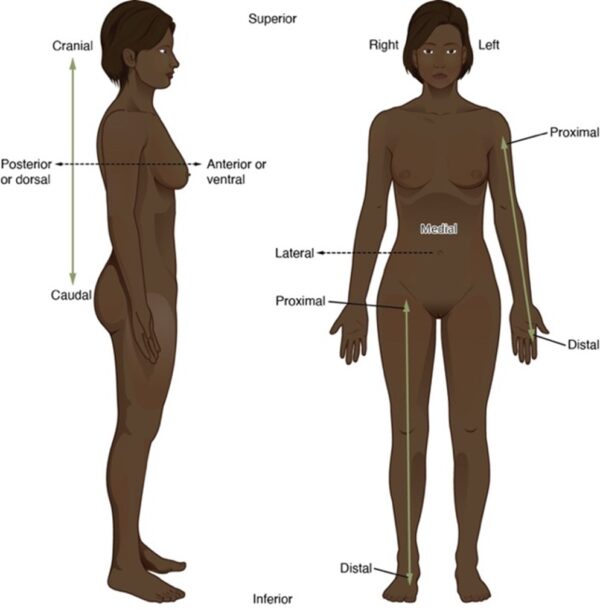
The anatomical position is used as a reference when describing locations of structures and movements. It is an upright position with arms by the side and palms facing forward. Feet are parallel with toes facing forward.
Anatomical terms
To understand anatomical planes, it is important to be familiar with basic anatomical terms:
- Proximal: towards the main trunk of the body
- Distal: away from the main trunk of the body
- Superior: upper
- Inferior: lower
- Superficial: near the surface of the body
- Deep: away from the surface of the body
- Medial: towards the midline
- Lateral: away from the midline
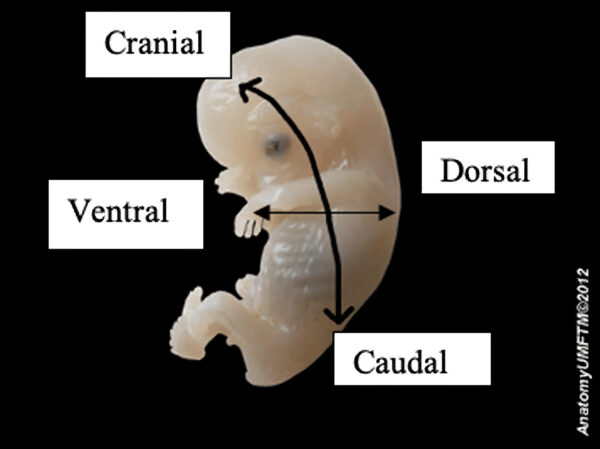
Additional terms which are more commonly used in embryology and neuroanatomy:
- Ventral: front, anterior
- Dorsal: back, posterior
- Cranial: towards the head
- Caudal: towards the ‘tail’ end
Clinical relevance: describing injuries
It is important to become familiar with anatomical terms to describe locations of bodily structures and injuries as well as for describing movements.
For example, Figure 3 shows a laceration located on the medial aspect of the 4th digit of the left hand immediately distal to the proximal interphalangeal joint.

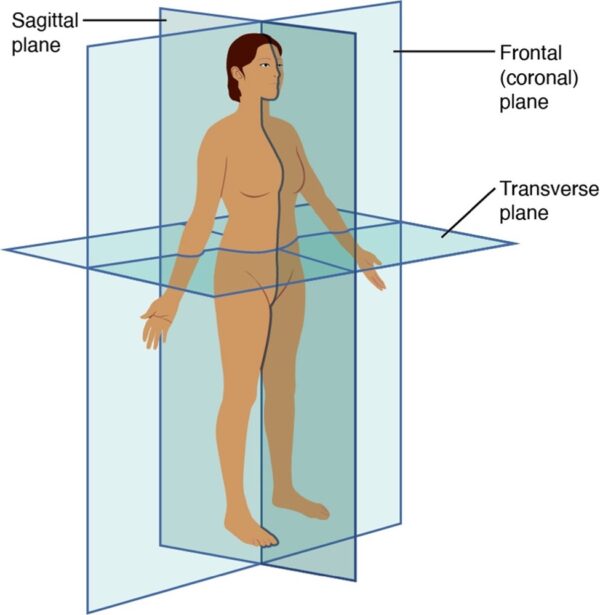
Anatomical planes
There are three commonly used anatomical planes: sagittal, coronal and axial (Figure 4).
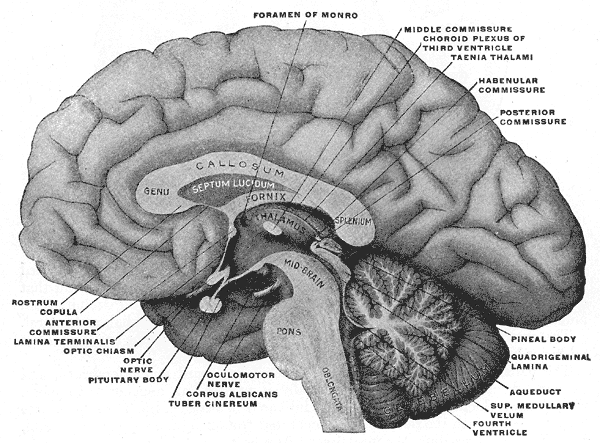
Sagittal
The sagittal plane is a longitudinal plane, dividing the body into right and left parts. These are not necessarily equal but if they are equal the plane is termed a midsagittal or median plane.
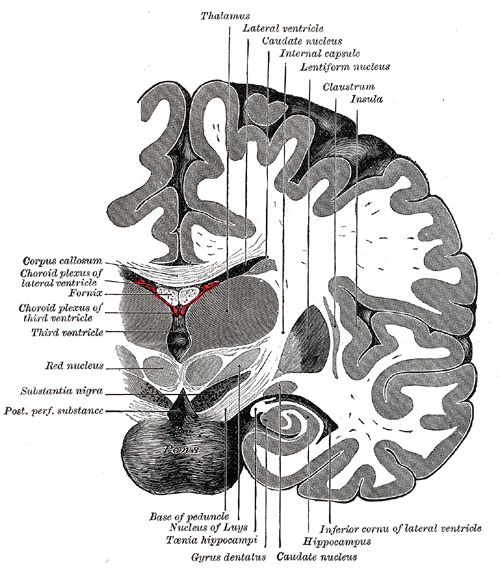
Coronal
The coronal plane is a longitudinal plane, dividing the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) sections.
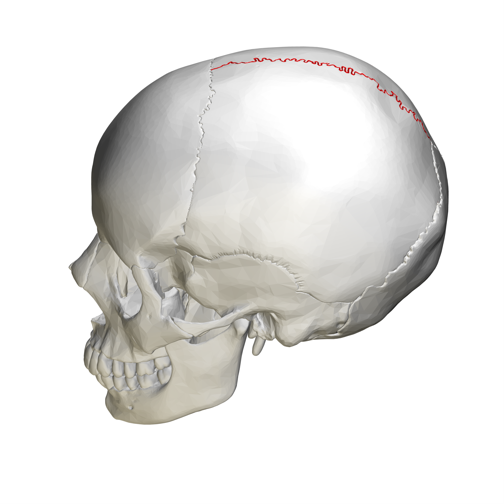
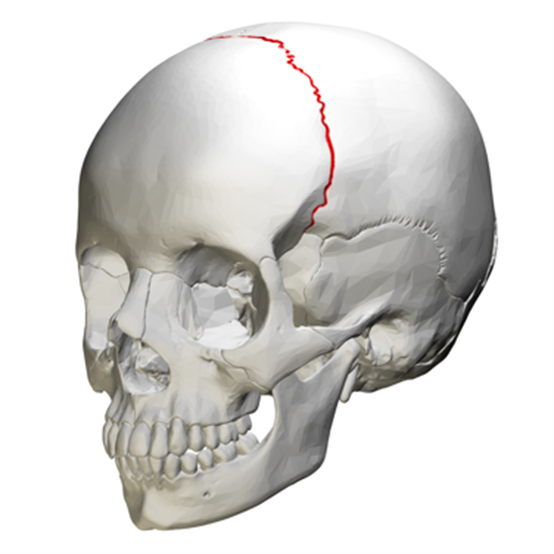
Clinical relevance: skull sutures
Sagittal and coronal are also terms used to describe the sutures of the skull. The original meaning of sagittal is ‘arrow’ and coronal means ‘crown’. It can be helpful to remember this when describing the anatomical planes.
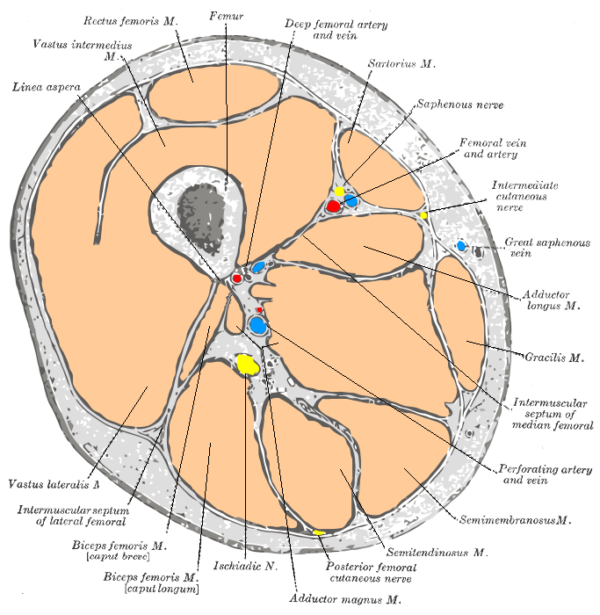
Axial
The axial (or transverse plane) is a horizontal plane dividing the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) sections.
Planes that are not parallel to any of the three planes above are termed oblique planes.
Clinical relevance: imaging investigations
Radiological images such as CT and MRI scans are viewed in different anatomical planes. It is important to understand the anatomical planes to orientate oneself to the images.
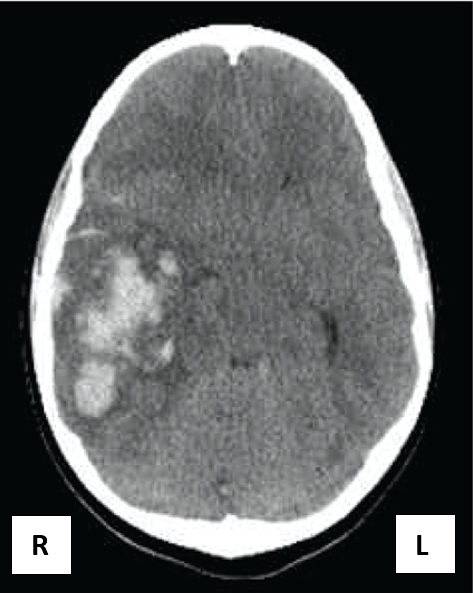
Axial CT and MRI images are viewed from the inferior aspect as if looking at a patient from the foot of the bed.
For example, Figure 8 shows a haemorrhagic stroke in the right hemisphere.
Key points
- Anatomical terms and planes help to describe locations of body structures and movements.
- Understanding the anatomical planes enables you to correctly orientate prosections and scans (e.g. CT).
Reviewer
Eva Sweeney, PhD
Lecturer (Anatomy)
Editor
Dr Chris Jefferies
References
- Anatomist90. Human embryo. License: [CC BY-SA]
- OpenStax. Anatomical terms applied to the human body. License: [CC BY]
- Jordan, R. Laceration of left 4th digit.
- OpenStax. Planes of the human body. License: [CC BY]
- Henry Vandyke Carter. Sagittal section of the brain. License: [Public domain]
- Henry Vandyke Carter. Coronal section of the brain. License: [Public domain]
- BodyParts3D/Anatomography. Sagittal suture. License: [CC BY-SA JP]
- BodyParts3D/Anatomography. Coronal suture. License: [CC BY-SA JP]
- Henry Vandyke Carter. Axial section of the thigh. License: [Public domain]
- OpenStax. CT scan of a haemorrhagic stroke. License: [CC BY]