- 📖 Geeky Medics OSCE Book
- ⚡ Geeky Medics Bundles
- ✨ 1300+ OSCE Stations
- ✅ OSCE Checklist PDF Booklet
- 🧠 UKMLA AKT Question Bank
- 💊 PSA Question Bank
- 💉 Clinical Skills App
- 🗂️ Flashcard Collections | OSCE, Medicine, Surgery, Anatomy
- 💬 SCA Cases for MRCGP
To be the first to know about our latest videos subscribe to our YouTube channel 🙌
Introduction
In the realm of ophthalmology and systemic disease, the focus traditionally lies on retinal findings obtained through fundoscopy.
However, this article takes a different approach, shifting the spotlight to ocular features apparent from a general examination without needing specialised ophthalmic equipment.
This perspective is particularly relevant for medical students and general practitioners, who often rely on more general examination techniques in their initial patient assessments. By exploring these observable ocular signs and their associations with various systemic diseases, this guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how the eyes can reflect broader systemic diseases.
This article will cover various body systems, illustrating how simple observations of the eyes can offer valuable insights into a patient’s systemic health.
Cardiovascular system
Hyperlipidaemia
Xanthelasma
Cholesterol deposits under the skin.
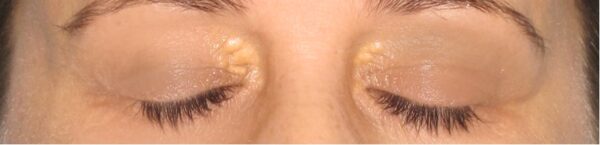
Corneal arcus
Lipid deposits on the outer cornea.
Gastrointestinal system
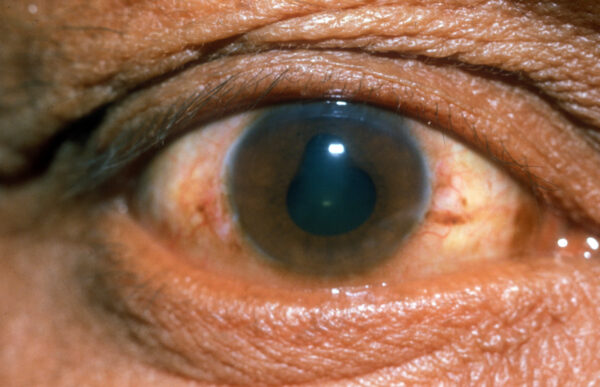
Wilson’s disease
Kayser-Fleischer rings
These form on the peripheral border of the cornea due to copper deposition.
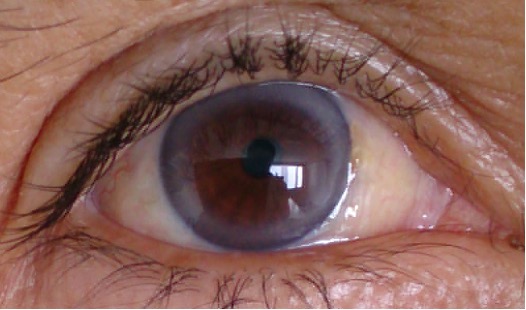
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis
Uveitis and episcleritis
The image shows an irregularly shaped pupil due to posterior synechiae in uveitis.
Nervous system
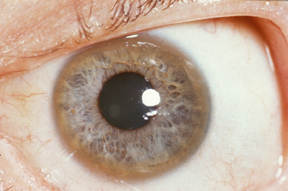
Neurofibromatosis type 1
Lisch nodules
Lisch nodules (iris hamartomas) are pathognomonic of neurofibromatosis type 1.
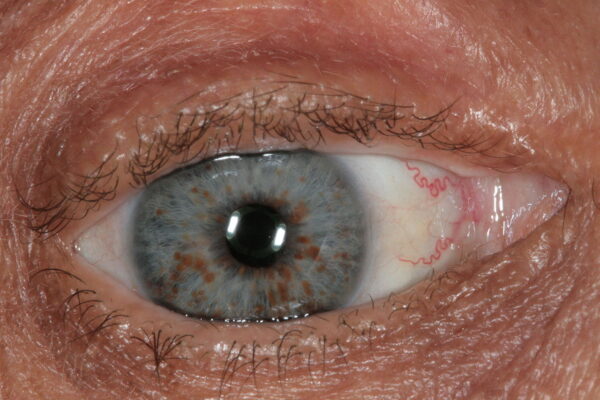
Endocrine system
Thyroid eye disease
Exophthalmos
There may also be lid lag on examination.
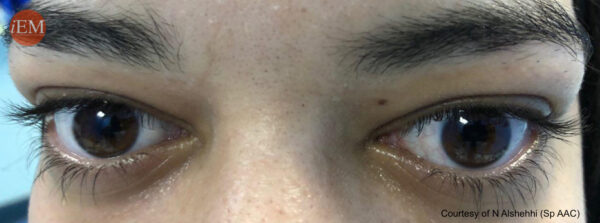
Dermatological conditions
Rosacea
Ocular rosacea
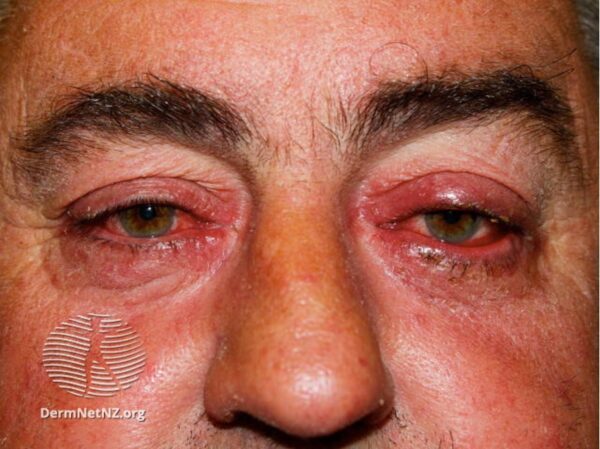
Autoimmune conditions
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis, Behçet’s disease and ankylosing spondylitis can cause dry, inflamed red eyes.
They are also associated with episcleritis, scleritis and uveitis. From general inspection, these likely appear as a non-specific, painful red eye.
Sarcoidosis can also be associated with conjunctival nodules.
Connective tissue diseases
Osteogenesis imperfecta and Ehler’s-Danlos syndrome
Blue sclera
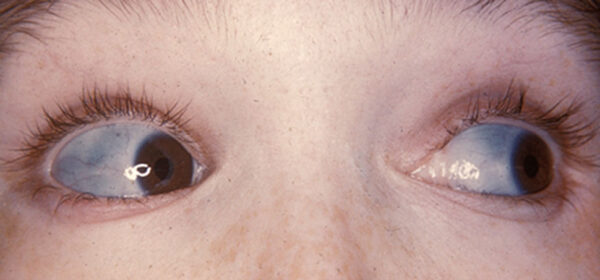
Marfan syndrome
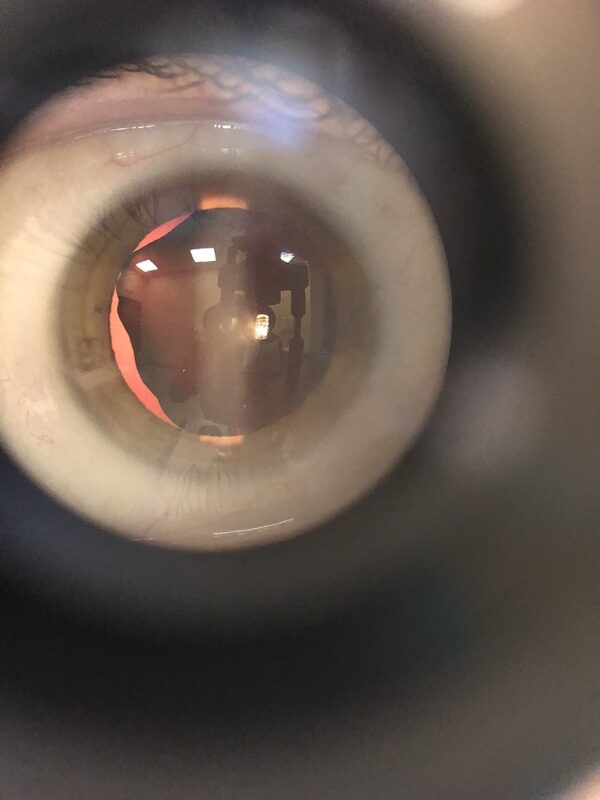
Lens subluxation
Marfan syndrome is associated with lens subluxation (ectopia lentis) when the lens is off-centre. It can occur in up to 75% of patients with Marfan syndrome. Lens subluxation is also associated with trauma and other ocular disease such as retinitis pigmentosa, high myopia and congenital glaucoma.
References
- American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ocular Manifestations of Systemic Disease. Published in 2009. Available from: [LINK]
- Patient.info. The Eye and Systemic Disease. Published in 2021. Available from: [LINK]
- Jacob J. Yunker, MD. Ocular Manifestations of Systemic Disease. Available from: [LINK]
Image references
- Figure 1. Oleg Tymofii. Adapted by Geeky Medics. Eyelid Xanthelasma. License: [CC BY-SA]
- Figure 2. Afrodriguezg. Arcus Senilis. License: [CC BY-SA]
- Figure 3. Herbert L. Fred, MD, Hendrik A. van Dijk. Kayser-Fleicher rings. License: [CC BY]
- Figure 4. Community Eye Care Journal. Posterior synechiae – a sign of uveitis. License: [CC BY-NC]
- Figure 5. Dimitrios Malamos. Lisch nodules. License: [CC BY]
- Figure 6. Emergency Medicine Clinical Images. Exophthalmos. License: [CC BY-NC-SA]
- Figure 7. Dermnet. Ocular rosacea. License: [CC BY-NC-ND]
- Figure 8. Herbert L. Fred, MD and Hendrik A. van Dijk. Characteristically blue sclerae of patient with osteogenesis imperfecta. License: [CC BY-SA]
- Figure 9. Anselmuccifederico. Subluxation of the lens in human eye. License: [CC BY]




