- 📖 Geeky Medics OSCE Book
- ⚡ Geeky Medics Bundles
- ✨ 1300+ OSCE Stations
- ✅ OSCE Checklist PDF Booklet
- 🧠 UKMLA AKT Question Bank
- 💊 PSA Question Bank
- 💉 Clinical Skills App
- 🗂️ Flashcard Collections | OSCE, Medicine, Surgery, Anatomy
- 💬 SCA Cases for MRCGP
To be the first to know about our latest videos subscribe to our YouTube channel 🙌
Introduction
A 25-year-old woman visits her GP due to vaginal discharge. Work through the case to reach a diagnosis.
UK Medical Licensing Assessment (UKMLA)
This clinical case maps to the following UKMLA presentations:
- Urinary symptoms
- Vaginal discharge
History
Presenting complaint
“I’ve noticed some weird discharge in my underwear, and it hurts when I have a wee.”
History of presenting complaint
Vaginal discharge
How long has this been happening?
“About 5 days”
Have you noticed any change in the amount of vaginal discharge?
“Yeah, I think over the last few days it’s become a bit more than usual”
Have you noticed a change in the colour of the discharge?
“It seems a bit more cloudy than usual, and maybe a bit more grey?”
Have you noticed that the discharge has become watery or thickened recently?
“It’s thinner than usual”
Does the discharge have a strong smell?
“It smells quite strong and bad, it’s quite embarrassing.”
Have you noticed any vaginal bleeding?
“No”
Dysuria
Characterise the pain using SOCRATES
“It burns when I wee and I also get a bit of discomfort in my lower tummy. It started pretty gradually over the last week, probably about 3/10.”
Have you been passing water more frequently?
“I think I’ve been going slightly more, but I’ve been drinking more too in case it was a water infection”
Have you been waking up from sleep with the need to pass water?
“No”
Have you noticed a change in the appearance of the urine?
“No”
Have you had any accidents?
“No”
Other parts of the history
Past medical and surgical history
- Do you have any medical problems?
“I’ve got asthma, but it’s really mild”
Specifically ask:
- Have you had any gynaecological issues before? (e.g. ectopic pregnancy, previous STIs, endometriosis, malignancy, gynaecological surgery)
- Have you ever been pregnant? If yes, clarify gravidity and parity
- Have you had your HPV vaccination?
- Do you attend cervical screening?
“I’ve not had any issues before and I’ve never been pregnant. I’ve had my HPV vaccine and had my first smear test this year – it was normal”
Medication history/allergies
- Do you take any regular medication?
- Do you have any allergies?
“I just have a salbutamol for my asthma but don’t really use it. I’m not allergic to anything”
Family history
- Do any medical problems run in the family?
“Not that I know of”
Menstrual history
- Do you currently menstruate?
- When was your last menstrual period?
- How long is your menstrual cycle?
- What are your menstrual periods like? (Ask about pain, duration, the volume of blood, presence of clots, etc)
“I haven’t had a normal period for years because I’ve been on the pill. I get my withdrawal bleeding but it’s been normal.”
Social history
- Do you live with anyone?
- Do you work or study currently?
- Do you smoke?
- Have you ever smoked?
- Do you drink alcohol? If yes, how many drinks would you say you have in a week?
- Do you use recreational drugs?
“I’m studying for my masters at the moment and live with my coursemate. I don’t smoke or drink and I try to keep very healthy”
Are you currently sexually active?
“Yes”
If the patient is currently sexually active then the following questions are important in a sexual history:
- When did you last have a sexual encounter?
- Was this sexual encounter consensual?
- Was this a regular sexual partner, or a casual sexual encounter?
- What sex was the partner in question?
- What type of sex was involved in this sexual encounter?
- Did you give or receive oral sex?
- Did you have vaginal sex?
- Did you give or receive anal sex?
- Did you take drugs just before or during sex?
- Did the sex involve more than two people?
- Did you use any form of contraception for the sexual encounter?
- Was any barrier contraception used during sex?
- Were there any issues with the contraception used? (e.g. condom splitting)
- Was there any point at which contraception was not used during the sex?
- Did you use contraception for every sexual encounter with this individual?
If the patient has multiple sexual partners, then the above details should be clarified for each partner.
“I’m in a monogamous relationship with my boyfriend, but I’m worried he’s cheating on me. We last had sex a few days ago and have sex about 3 times a week. Only vaginal and oral sex. I’ve been taking the pill for a few years now so we don’t use a condom.”
Clinical examination
Examination findings
- Inspection: vulval redness, thin white discharge on the vaginal walls and speculum. There is an offensive smell to the discharge
- Palpation: no irregularities in the vaginal wall, fornices or cervix
- Normal anteverted uterus.
Inspection of the cervix
An image of the patient’s cervix is shown below.
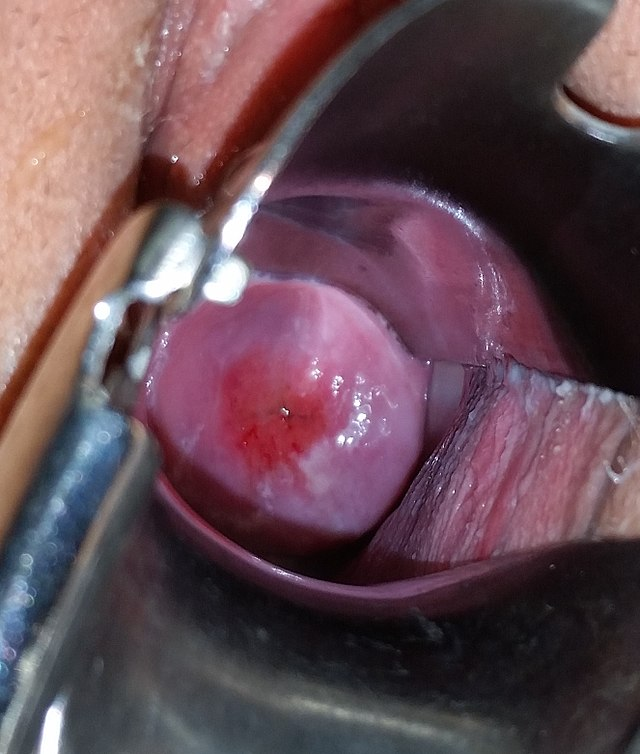
There is an area of redness surrounding the external os.
This is a cervical ectropion, an often benign condition in which columnar epithelia is present on the outside of the vaginal cervix (appearing red), as opposed to just inside the cervical canal.
A cervical ectropion is often clinically asymptomatic and does not require treatment. However, due to the network of fine blood vessels, patients may present with post-coital bleeding.
Investigations
- Urinalysis: to look for raised leucocytes in infection, presence of nitrites in UTI, haematuria
- Urine beta HCG: to exclude pregnancy
- Vulvo-vaginal/endocervical NAAT swabs for chlamydia/gonorrhoea
- High vaginal/endocervical charcoal media swab for bacterial vaginosis, trichomonas vaginalis, candida and Group B streptococcus
- Vaginal litmus test (if available)
Diagnosis
Swab sample
Swab samples were viewed under microscopy.
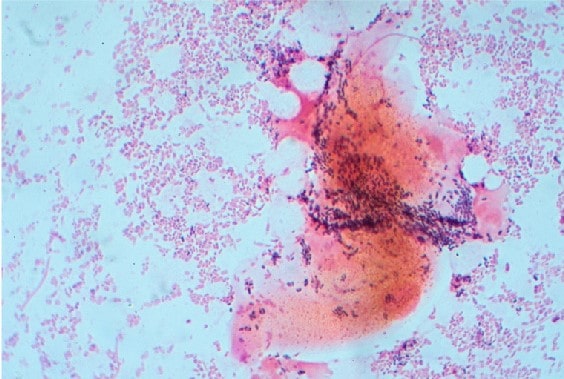
This image shows clue cells. These are vaginal epithelial cells that have been Gram stained (pink), which shows the cells covered with bacteria (purple).
This patient has presented with the typical symptoms of an increase in vaginal discharge, thinner than usual and offensive smelling. The swabs also show the presence of clue cells on microscopy, which are strongly associated with bacterial vaginosis.
Management
- BV is usually self-limiting and resolves after 3-7 days.
- Treatment may not be necessary if it is asymptomatic
Avoid factors that raise vaginal pH, such as:
- Vaginal douching, deodorant, and washes
- Bubble baths, shampoos near the genitals
- Presence of semen in the vagina
Some patients find probiotics useful. This can be in dietary intake (kimchi, kefir, kombucha, etc), tablet or vaginal pessary. Research suggests this can be useful, though there is no conclusive evidence yet.
The recommended antibiotic is oral metronidazole 400-500 mg BD for 5-7 days.
Editor
Dr Jess Speller
References
- GynaeImages. Adapted by Geeky Medics. Cervical ectropion. Licence: [CC BY-SA]
- Dr Graham Beards. BV flora. License: [CC BY-SA]
- NICE CKS. Bacterial Vaginosis. Available from: [LINK]
- BMJ Publishing Group (2018) Overview of sexually transmitted diseases, Available from: [LINK]




